Catching Problems Early
Proactive maintenance helps technicians get ahead of potential vehicle breakdowns. There are scheduled dates for inspection and the maintenance of critical parts.
Critical parts such as the transmission system, braking system, steering and suspension systems, wheels, tires, the exhaust system, the electrical system, belts and hoses, and other critical parts are inspected for any defects.

If a replacement is needed, a new part is installed and the date is accurately recorded. Reactive maintenance focuses on restoring equipment to its normal operating condition.
Emergency repairs cost up to 6 times more than planned repairs, so maintenance plans that rely on reactive maintenance are generally the most expensive.
Reactive maintenance can be very costly indirectly. Parts that have failed must be ordered, shipped, and delivered. Depending on availability, a replacement part can take days or weeks to arrive.
Vehicle downtime due to parts availability has a big impact on overall operating costs. These shipment delays force many companies to work more hours and pay overtime expenses to meet deadlines.
In 2017, repair shops spent 32% more on reactive maintenance than on regularly scheduled preventative maintenance.
Creating a Detailed Service Log
A detailed service log records important maintenance information.
It’s one of the first steps to developing a preventative maintenance plan.
Businesses that keep detailed maintenance records can go back and identify wastefulness. They can analyze this information and find opportunities to save money.
A service log also provides visibility and makes everyone accountable for their work.
To begin outlining your service log, start by listing the criteria most important to your maintenance objectives.
Draft a mission statement of what your plan seeks to achieve. Next, define how your team will be scheduling maintenance.
How will your team stay organized? Who will be responsible for record keeping?
Does your maintenance plan keep track of mileage, important maintenance dates, and other vehicle usage information?
The chart below is a good example of an organized and detailed service log.
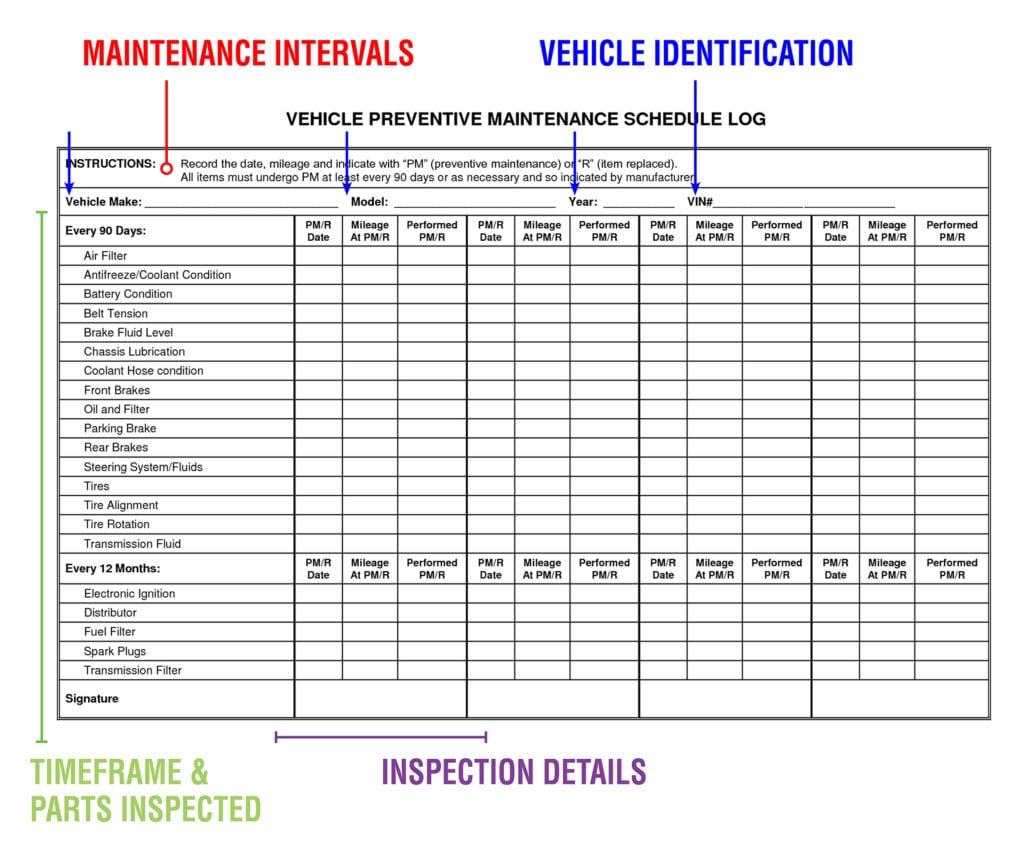
Once you’ve fleshed out your detailed maintenance log, your team can review the data and look for opportunities to save money.
Here are some important questions your team should ask going forward:
- What does our maintenance workflow look like?
- Where in the maintenance process can our company save money and eliminate costs?
- Which repairs are the most expensive and time-consuming?
- Can preventative maintenance stop costly repairs?
- What can be done to reduce the chance of mechanical failure?
Repeatability is the most important element of a preventative maintenance plan.
If your team isn’t faithfully collecting data, then you’re wasting your time. Cost patterns are only apparent when there’s enough collected data to flag recurrent expenses.
Remember: Preventative Maintenance is about optimizing how a company manages its expenses. Finding opportunities to fix problems before they get out of hand reduces costs and frees up resources for business development.






